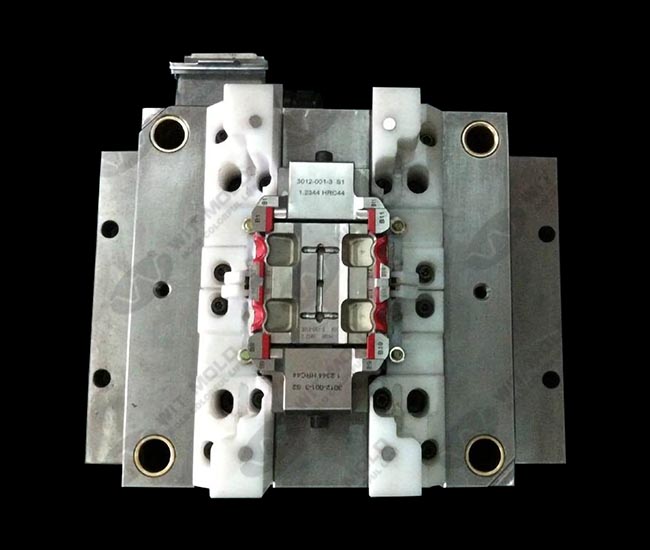
Inserted molding tools play a critical role in modern plastic manufacturing, enabling the integration of metal or other rigid inserts directly into molded plastic parts. This technology is widely used in automotive, electronics, medical, and industrial applications where strength, accuracy, and reliability are essential.
What Are Inserted Molding Tools?
Inserted molding tools are specialized injection molds designed to hold metal or non-plastic inserts in precise positions before molten plastic is injected around them. Once cooled, the plastic and insert form a single, integrated component.
The insert may be:
-
Metal (brass, steel, stainless steel, copper)
-
Threaded components
-
Electrical contacts or terminals
-
Bushings, pins, or reinforcement parts
These tools are engineered to ensure insert stability, accurate alignment, and consistent over-molding quality during high-volume production.
How Inserted Molding Works
-
Insert Placement
Inserts are positioned into the mold cavity manually or via automated systems such as robotic arms. -
Mold Closing & Injection
The mold closes, and molten plastic is injected, encapsulating or partially surrounding the insert. -
Cooling & Solidification
The plastic cools and bonds mechanically (and sometimes chemically) with the insert. -
Ejection
The finished part is ejected as a single, structurally integrated unit.
Precision tooling design ensures inserts do not shift during injection, which is crucial for dimensional accuracy.
Key Advantages of Inserted Molding Tools
1. Improved Mechanical Strength
By embedding metal inserts directly into plastic, components gain enhanced load-bearing capacity, wear resistance, and durability.
2. Reduced Assembly Steps
Insert molding eliminates secondary operations such as pressing, welding, or fastening, lowering labor costs and improving production efficiency.
3. High Dimensional Accuracy
Inserted molding tools ensure repeatable positioning of inserts, which is critical for threaded parts, electrical contacts, and precis
ion assemblies.
4. Better Product Reliability
Integrated structures reduce the risk of loosening, misalignment, or failure during long-term use.
5. Cost Efficiency at Scale
While tooling investment may be higher initially, mass production significantly reduces per-unit cost.
Common Applications of Inserted Molding Tools
Automotive Industry
-
Sensor housings
-
Electrical connectors
-
Threaded plastic fasteners
-
Structural interior components
Electronics & Electrical
-
Terminal blocks
-
Switch housings
-
Connectors with embedded contacts
-
Insulated conductive components
Medical Devices
-
Surgical instrument handles
-
Diagnostic equipment housings
-
Precision connectors requiring strength and hygiene
Industrial Equipment
-
Knobs, handles, and control parts
-
Load-bearing plastic components
-
Wear-resistant assemblies
Key Design Features of Inserted Molding Tools
High-quality inserted molding tools typically include:
-
Insert Locating Mechanisms
Precision pockets, pins, or magnetic fixtures to hold inserts securely during injection. -
Heat Management Design
Controlled heating and cooling to prevent insert movement and material stress. -
Anti-Rotation & Anti-Float Structures
Prevent inserts from spinning or lifting under injection pressure. -
Automation Compatibility
Designed for robotic insert loading to support high-volume, consistent production. -
High-Durability Mold Steel
Ensures long tool life under repeated thermal and mechanical stress.
Inserted Molding vs Overmolding
While often confused, the two processes differ:
-
Inserted Molding:
Inserts are placed into the mold first, then plastic is injected around them. -
Overmolding:
Plastic is molded over an existing plastic or rubber substrate.
Inserted molding tools are ideal when rigid reinforcement or electrical functionality is required.
Important Factors When Choosing Inserted Molding Tools
Buyers and engineers typically consider:
-
Insert material and geometry
-
Required tolerances and alignment accuracy
-
Plastic resin compatibility
-
Production volume and automation level
-
Mold lifespan and maintenance requirements
-
Compliance with industry standards (automotive, medical, electrical)
Proper tool design directly affects product quality and production efficiency.
Conclusion
Inserted molding tools are essential for manufacturing high-strength, multifunctional plastic components with integrated inserts. By combining precise tooling design with efficient injection molding, manufacturers can achieve superior performance, reduced assembly costs, and consistent quality at scale.
For industries requiring durable, accurate, and production-ready plastic parts, insert molding tools offer a proven and cost-effective solution.